While blood clotting is a necessary process that can keep people from losing too much blood following an injury, a clot that forms inside of your veins doesn’t always dissolve on its own, which can lead to a dangerous and even life-threatening situation. Blood clots form to try to repair damage to a blood vessel, in the form of a gel-like mass in the blood to stop bleeding. When they form inappropriately inside an artery or vein, they can cause problems due to a lack of blood flow.
When a clot occurs in one of the major veins deep inside the body, it is known as deep vein thrombosis or DVT. DVT is most common in the legs, but it can also happen in the arms, pelvis, lungs and even the brain. A blood clot that is immobile usually isn’t harmful, but if it happens to break free, it can travel through the veins to the heart and lungs where it may get stuck and prevent blood flow. A blood clot that travels to the lungs is known as a pulmonary embolism, which is a severe medical emergency.
According to the American Society of Hematology, DVT affects an estimated 900,000 Americans each year, killing up to 100,000 of them. It’s extremely important that you see a health care professional if you believe you may have a blood clot—but the only way to recognize when you need medical help is to learn about the most common symptoms and risk factors.
Risk Factors
There are several known risk factors that increase the chances of developing a blood clot. A recent major surgery or long stay in the hospital can increase your risk, as well as:
- Age – especially being older than 65
- Lengthy travel – trips that caused you to sit for more than four hours at a time
- Bed rest or being sedentary for long periods of time
- Obesity
- Pregnancy
- Family history of blood clots
- Smoking
- Certain birth control pills
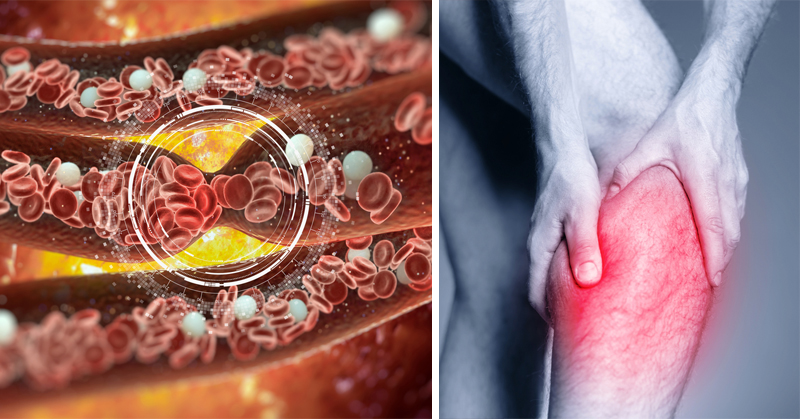
Blood Clot in the Leg
This is a scary thought, but it’s possible to have a blood clot with no obvious signs or symptoms, and some symptoms are often the same as in other diseases. But the most common place for a blood clot to occur is in the lower leg. The symptoms depend on the size of the clot. A large clot can cause extreme swelling and intensive pain in the leg. Symptoms of a blood clot in the leg can include:
- Swelling
- Pain
- Tenderness
- A warm sensation
- Pain in the calf when you stretch your toes upward
- A pale or bluish discoloration

Blood Clot in the Heart
It is less common for a blood clot to occur in the heart, but it can still happen. A blood clot in the heart could cause your chest to hurt or feel heavy, and be accompanied by feeling light-headed and experiencing shortness of breath.
Blood Clot in the Abdomen
Signs of a blood clot in the abdomen can include severe abdominal pain accompanied by vomiting and diarrhea. These could also be symptoms of a stomach virus or food poisoning, so be sure to check in with a health care professional.
Blood Clot in the Brain
A sudden and severe headache along with sudden difficulty seeing or speaking could be signs of a blood clot that has formed in the brain.
Blood Clot in the Lungs
Possible signs of a blood clot that has traveled to the lungs (a pulmonary embolism) include:
- Sudden shortness of breath that can’t be explained
- Chest pain
- Heart palpitations or rapid heart rate
- Breathing problems
- Coughing up blood
Additional complications of a blood clot can include a heart attack, stroke, kidney failure, and pregnancy problems. Work to control your risk factors by maintaining a healthy weight, staying active and refraining from smoking. If you think you may have a blood clot, it’s important to call a health care professional right away. Symptoms that appear out of the blue, especially sudden shortness of breath, chest pressure and difficulty breathing, seeing or speaking should be considered an emergency.
h/t: heathline